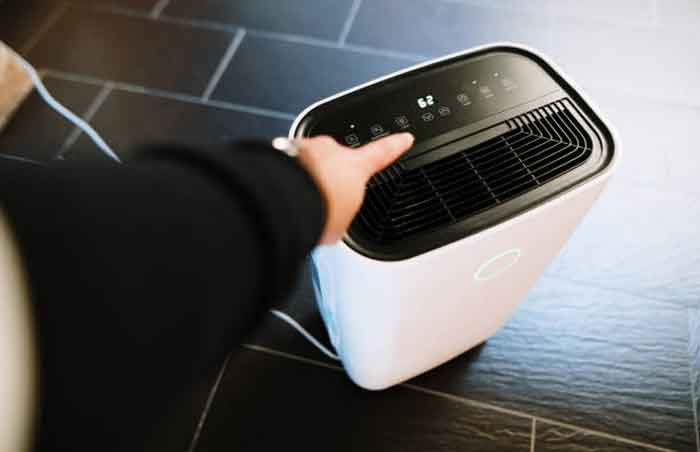
A commercial dehumidifier is a great way to reduce the humidity in your business, home, or other location. It removes water by using a combination of the Adsorption and Refrigeration principles to draw water from your air. Learn how these two processes work, and how to find the right one for your business.
Absorption principle

An air dehumidifier works by absorbing water from the air around it. The machine uses a rotating mechanism with vertical modules filled with desiccant. These modules are connected with tubes that allow the air to flow over them. The water absorbed by the desiccant is subsequently released as drier air.
The main difference between the two models is the way in which they remove moisture from the air. The adsorption model involves soaking up moisture from the air and spitting it out, while the condensation model involves using cooling. Typically, the larger the dehumidifier, the more air it can move. These dehumidifiers are more efficient when drying large spaces, such as a warehouse or industrial facility.
Condensate collection receptacle
The present invention is a low-profile, removable condensate collection receptacle designed for use with a dehumidifier. The receptacle includes a built-in fan for circulating the air. When the unit is turned on, the humid air flows into the evaporator. This cooling process creates condensate, which runs down to the receptacle.
Most portable dehumidifiers come equipped with a condensate collection receptacle. These containers typically have a float sensor that senses when the collection bucket is full. This feature prevents the collection vessel from overflowing and shutting down the dehumidifier. However, in warm and humid environments, collection buckets can fill up within eight to twelve hours. Therefore, you may need to empty the bucket several times per day.
Refrigeration principle
Commercial dehumidifier works by removing excess humidity from the air. This process is accomplished by running the air over a series of cold and hot coils. When the air reaches these coils, it condenses into water droplets. These droplets then fall into the water tank or drip tray. Afterward, the dehumidifier’s fan propels dry air out of the room.
In order to effectively eliminate humidity, the dehumidifier must have an additional heat sink. This heat sink is similar to the one in a conventional air conditioner. The dehumidifier must be sized appropriately to accommodate this additional heat sink.
Adsorption principle
A commercial dehumidification uses a process called adsorption to reduce humidity levels. The adsorption process releases heat into the air, which is then transferred to the desiccant material. The heat of adsorption is the sum of the latent heat of vaporization and the heat of wetting, which is released when water vapor makes contact with the surface of a desiccant.
Conclusion:
A typical dehumidifier consists of a large drum that is about as wide as the machine itself. The drum is an inch or two thick, and it is impregnated with a desiccant. This desiccant removes moisture from the incoming air by condensing the water vapor in it. The airflow that is condensed in this drum is then exhausted to the outside of the machine.